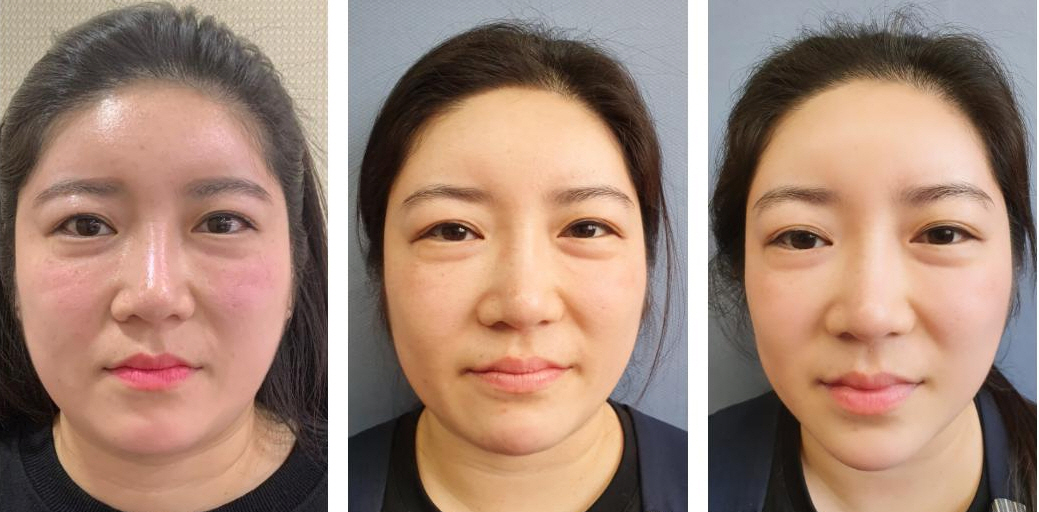
Lipolysis Solution is an aesthetic procedure solution type material that breaks down fats or lipids to remove unwanted fat tissue deposits in the body. It call as “Fat-Dissolving Solution” or “ Lipolytic Solution”.
3 Main Mechanisms of Lipolytic Solution
1. Increasing Energy Expenditure on Fat Tissue.
2. Regulation on Adipocyte Proliferation
3. Destruction of Adipocyte
3 Avoids to Use Lypolytic Solution
1. Irreversible Side Effects or Complications
2. Rebound and Short Term Effect
3. Severe System Adverse Effect
3 Ideal Lipolytic Solution
1. Long Term Effect
2. Less Complications & Side Effect
3. Easy Application
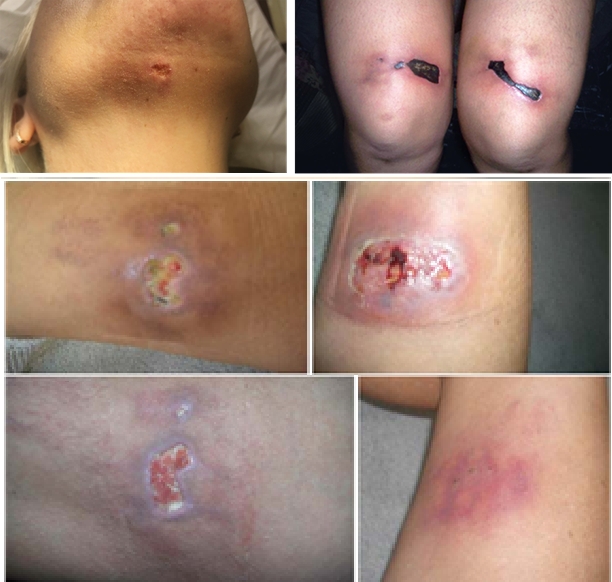
Protocol 1.Interval : several weeks 1.DESTRUCTION of ADIPOCYTE 1)Increase Energy Expendure https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2020.582781/full#F9 TRIAMCINOLONE _NONCONFIRMATIVE MECHANISM (Hypothesis) 1.The lymphatic spread of the corticosteroid suspension and resultant atrophy of the dermal and epidermal tissues. Triamcinolone acetonide suspended crystals enter and spread along lymphatic channels thus causing the linear ray distribution pattern. TRIAMCINOLONE
PHOSPHATIDYLCHOLINE ≒ LECITIN

Sessions: two to six treatments
2.Side Effects: The treated area after the procedure is red, swollen and sometimes slightly painful. In rare cases there can be bruising . After 3 days, usually all returns to normal.
3.Effect Onset Time : The first effect can be seen after 14 days and then fully after 6 weeks.
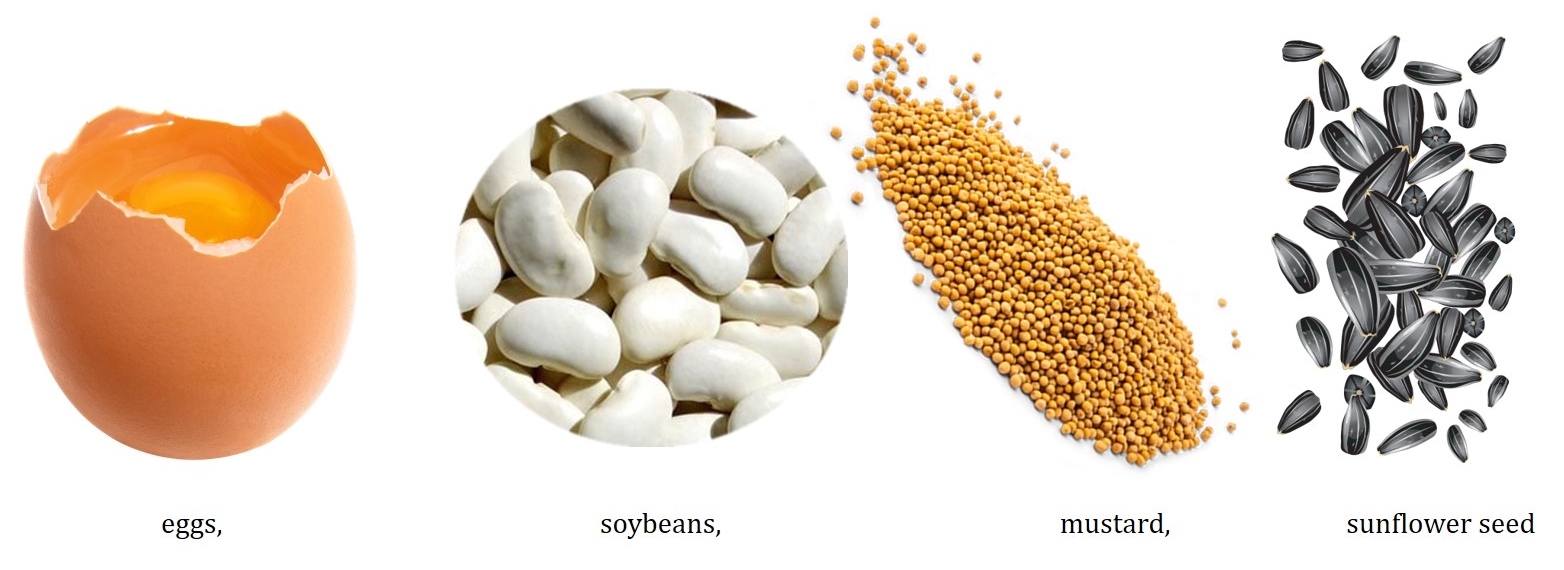
4.Contraindication : autoimmune disease, allergy to soya, diabetic vascular disease, severe liver or kidney disease, acute infections, blood clotting disorders , obesity and is not suitable for children, pregnant and breastfeeding women.
5.Recommends :
①Drink a lot of fluids, preferably non-carbonated water and vitamins, minerals and antioxidants, before treatment and during the first 3-5 days after treatment.
②Wearing loose clothes , in case of sensitivity of the treated area cooling the first 2 days is convenient.
③Evasion drink alcohol for 7days.
④Leave out physical exercises and avoid visiting sauna or solarium for 5days.
⑤Keep Physical activity and proper diet.
DEOXYCHOLIC ACID ≒ 2ndary Bile Acid
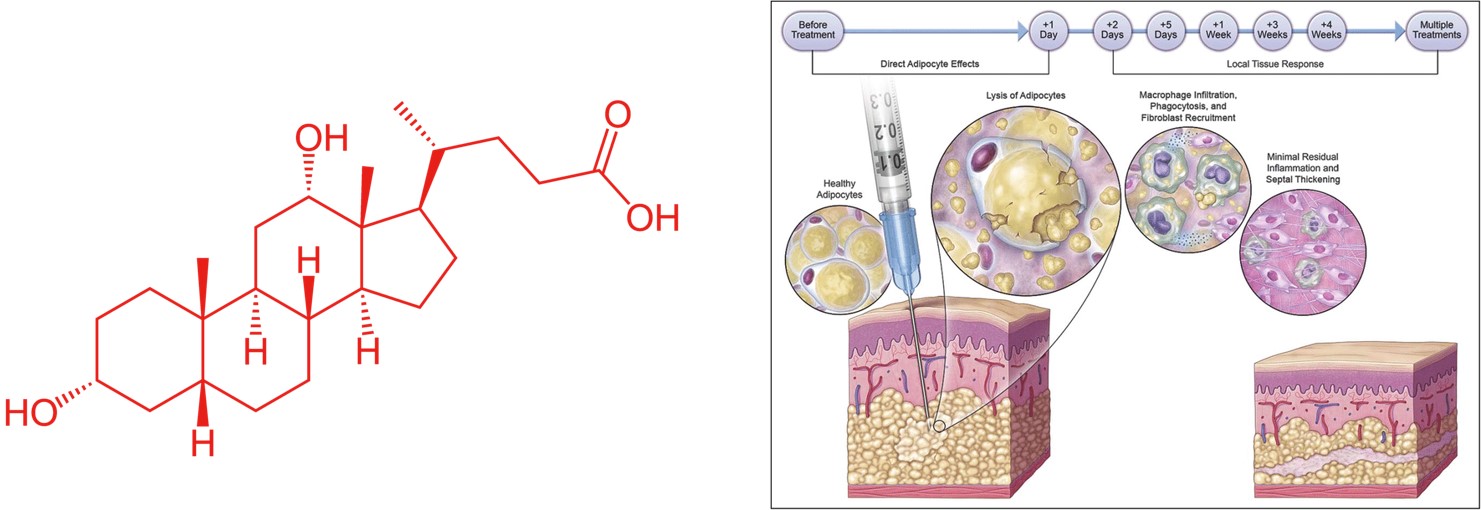
In research deoxycholic acid is used as a mild detergent for the isolation of membrane associated proteins. The critical micelle concentration for deoxycholic acid is approximately 2.4–4 mM.
Sodium deoxycholate, the sodium salt of deoxycholic acid, is often used as a biological detergent to lyse cells and solubilise cellular and membrane components. Sodium deoxycholate mixed with phosphatidylcholine, is used in mesotherapy injections to produce lipolysis, and has been used as an alternative to surgical excision in the treatment of lipomas.
In the United States, deoxycholic acid, under the trade name Kybella, is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for reducing moderate-to-severe fat below the chin. When injected into submental fat, deoxycholic acid helps destroy fat cells. Kybella is produced by Kythera Biopharmaceuticals.
PLANT EXTRACTS




NON-SPECIFIC ORIGIN
MEDICINE
TRIALED SOLUTION
ADIPOCYTE DIFFERENTIATION
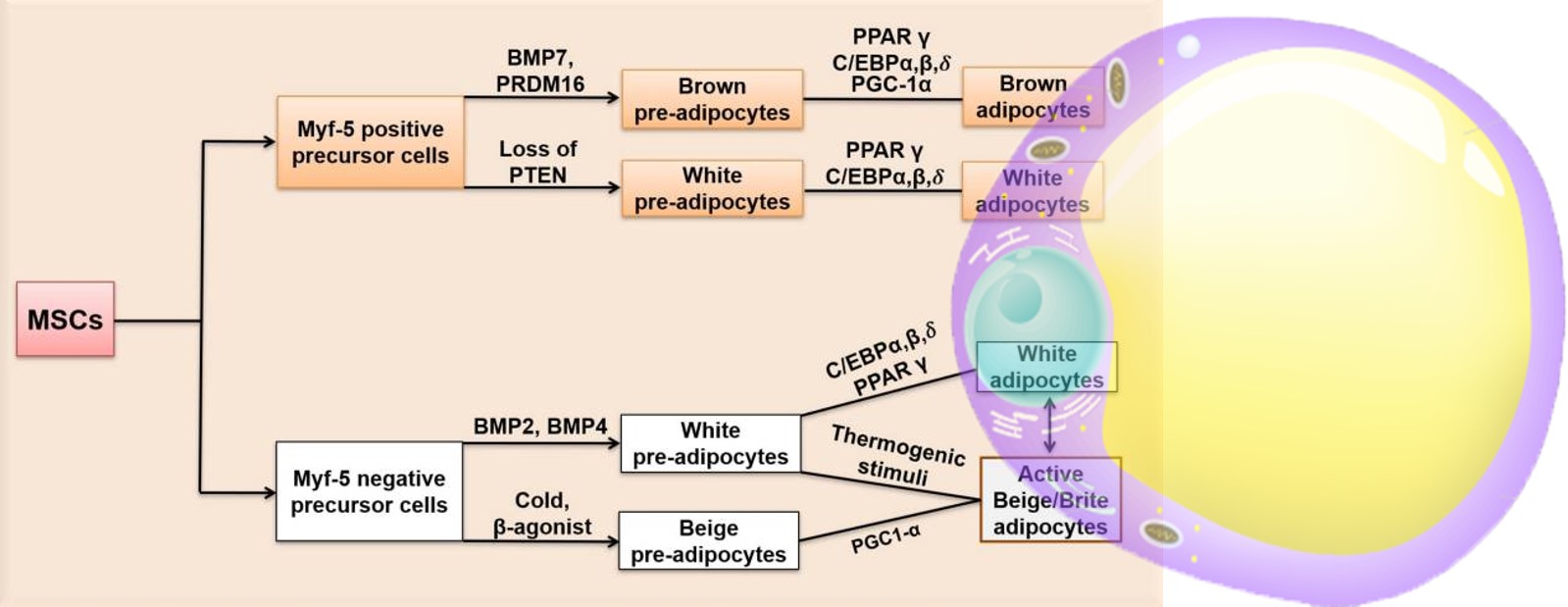
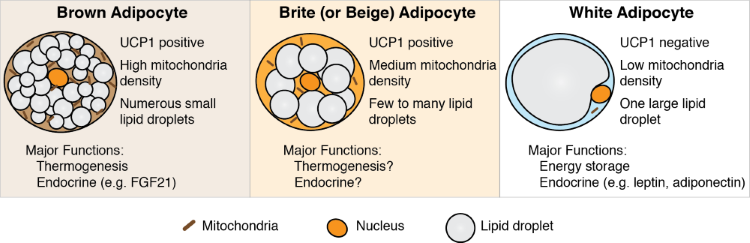
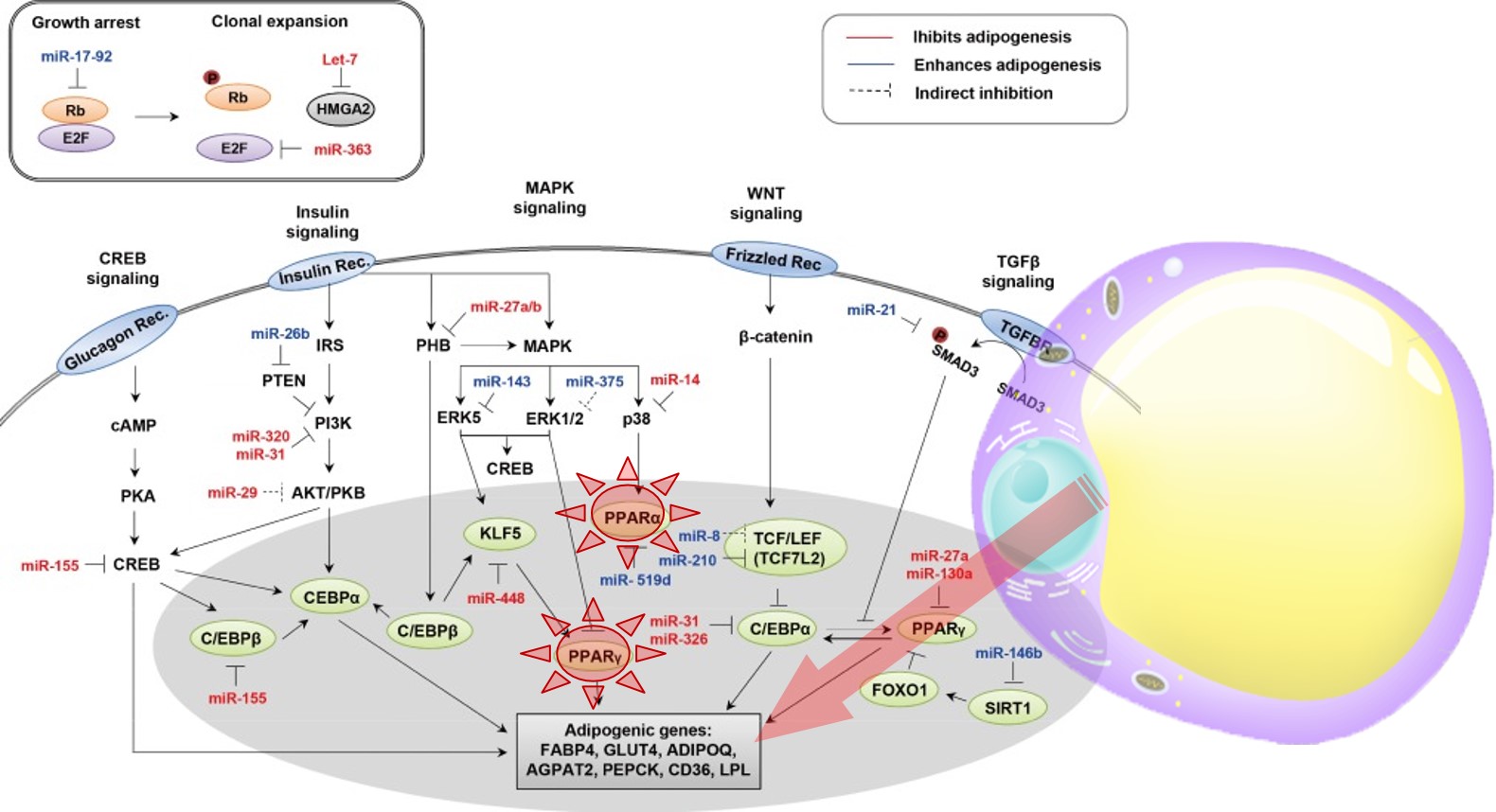
ADIPOGENIC GENE EXPRESSION
BASIC ADIPOCYTE METABOLISM
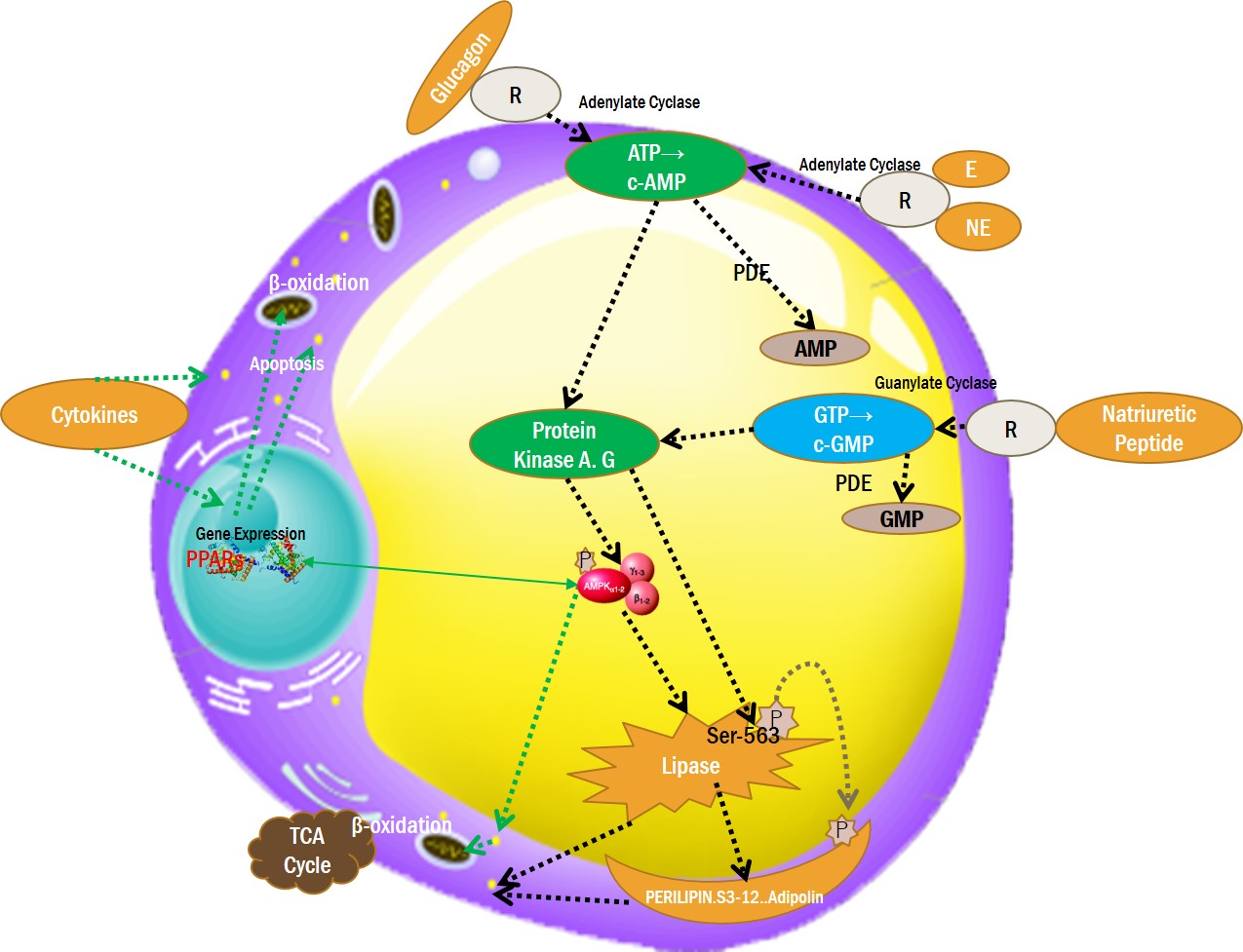
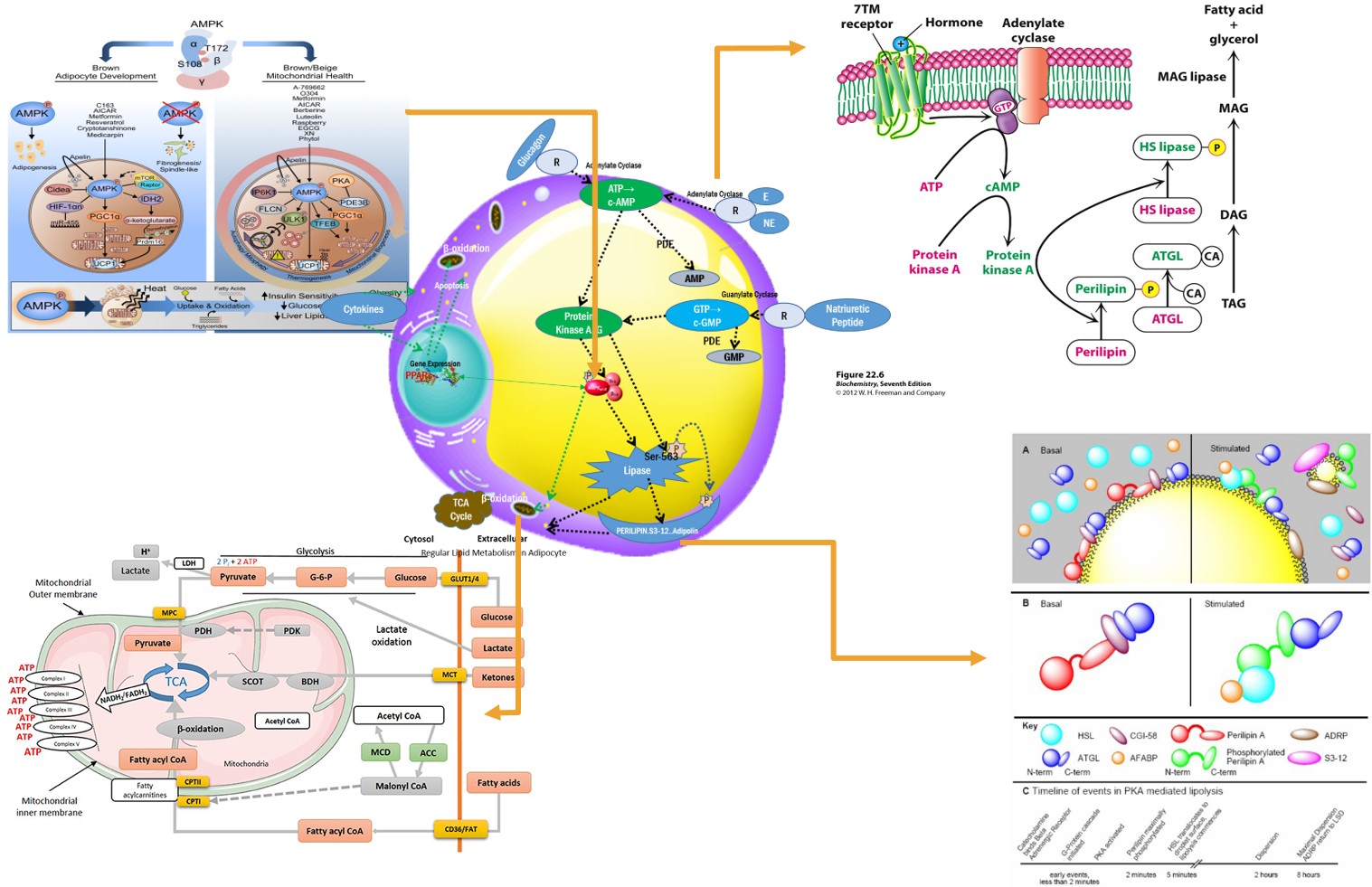
ADIPOCYTE MITOCHONDRIA ENERGY PRODUCTION

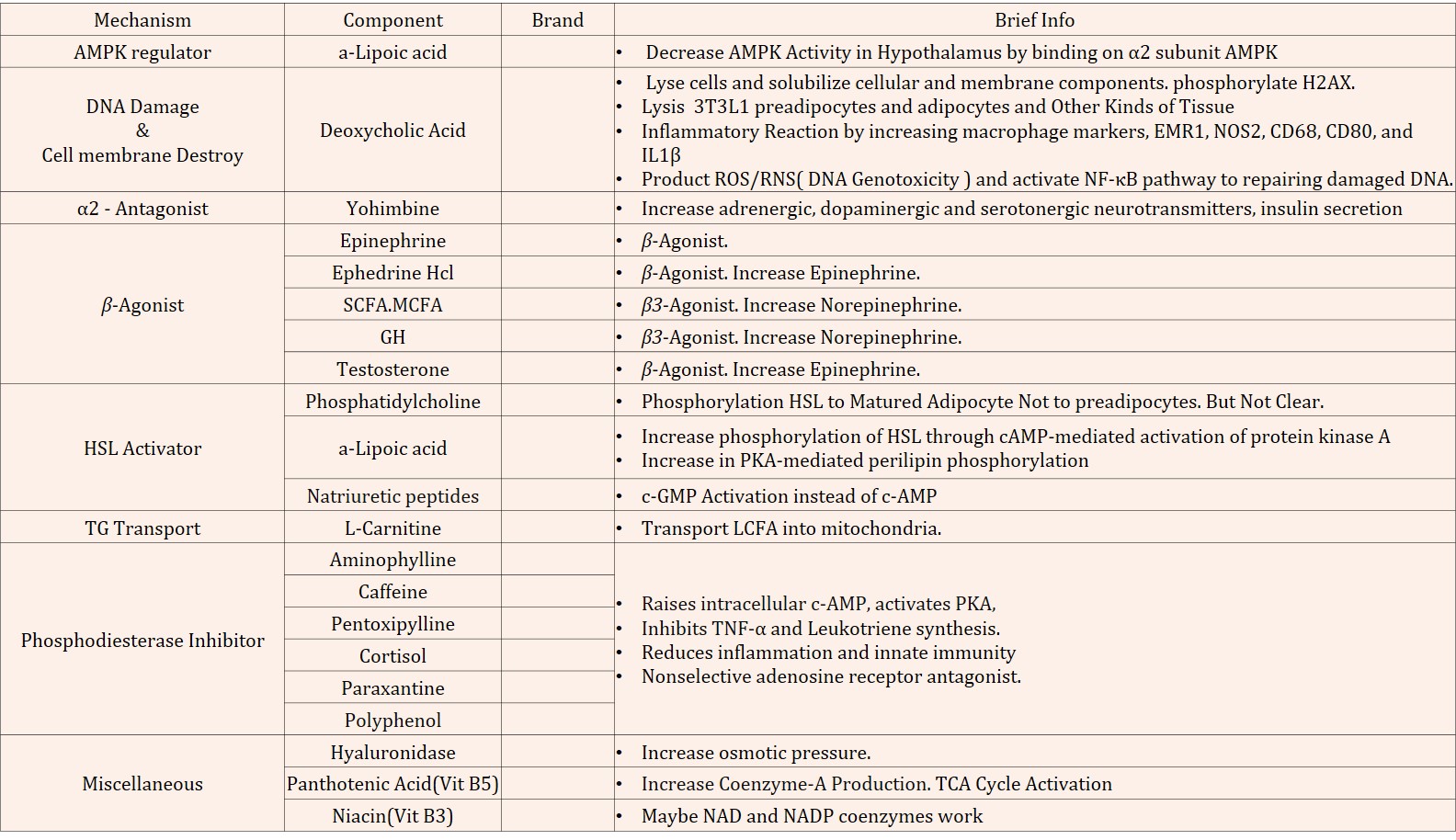
2.CYTOKINES INDUCED LIPOLYSIS
3.c-AMP, c-GMP INDUCED LIPOLYSIS
①β-ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST
②GLUCAGON RECEPTOR AGONIST
③NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE RECEPTOR AGONIST
④ADENYLATE & GUANYLATE CYCLATE ACTIVATOR
⑤PDE(Phosphodiesterase) INHIBITORS
4.Protein Kinases (PKA,PKD) Activating LIPOLYSIS
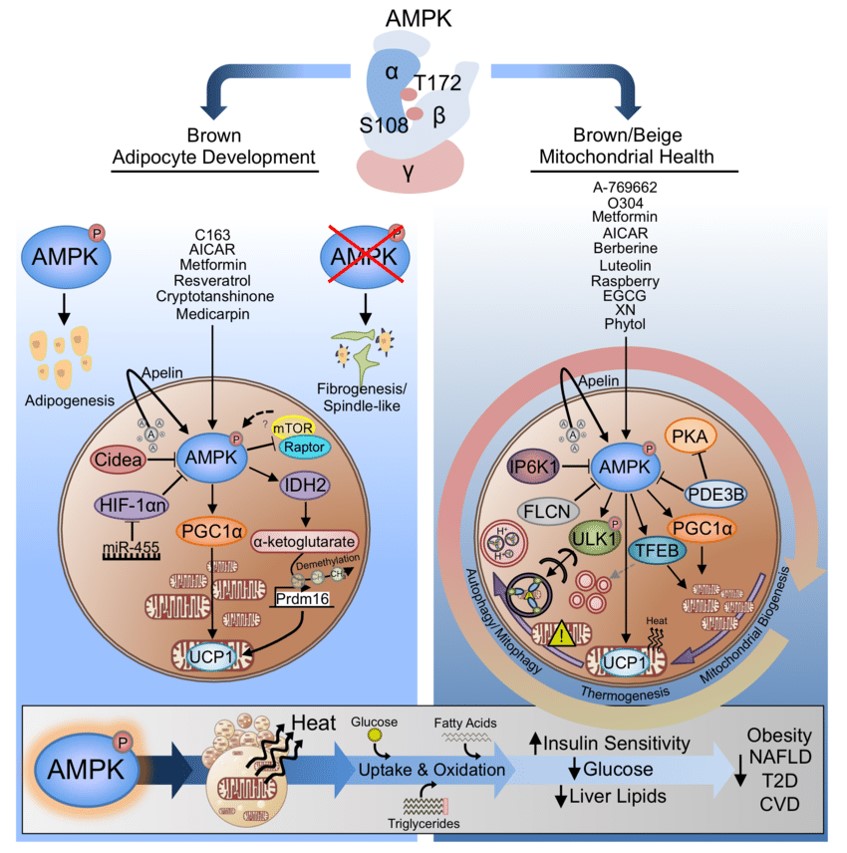
5.AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) LIPOLYSIS
6.PPARs INDUCED LIPOLYSIS
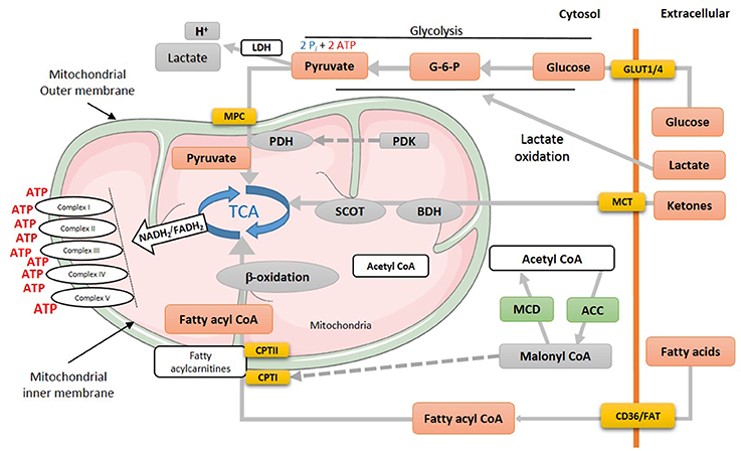
7.MITOCHONDRIA ENERGY PRODUCTION LIPOLYSIS
8.MISCELLANEUS ORIGN
9.LIPOLYSIS TARGET POINTs
2)Supply FA to Mitochondria
3)Change WFA to BAT
4)Suppress Adipocyte Genesis
1. DESTRUCTION of ADIPOCYTE
Deoxycholic Acid
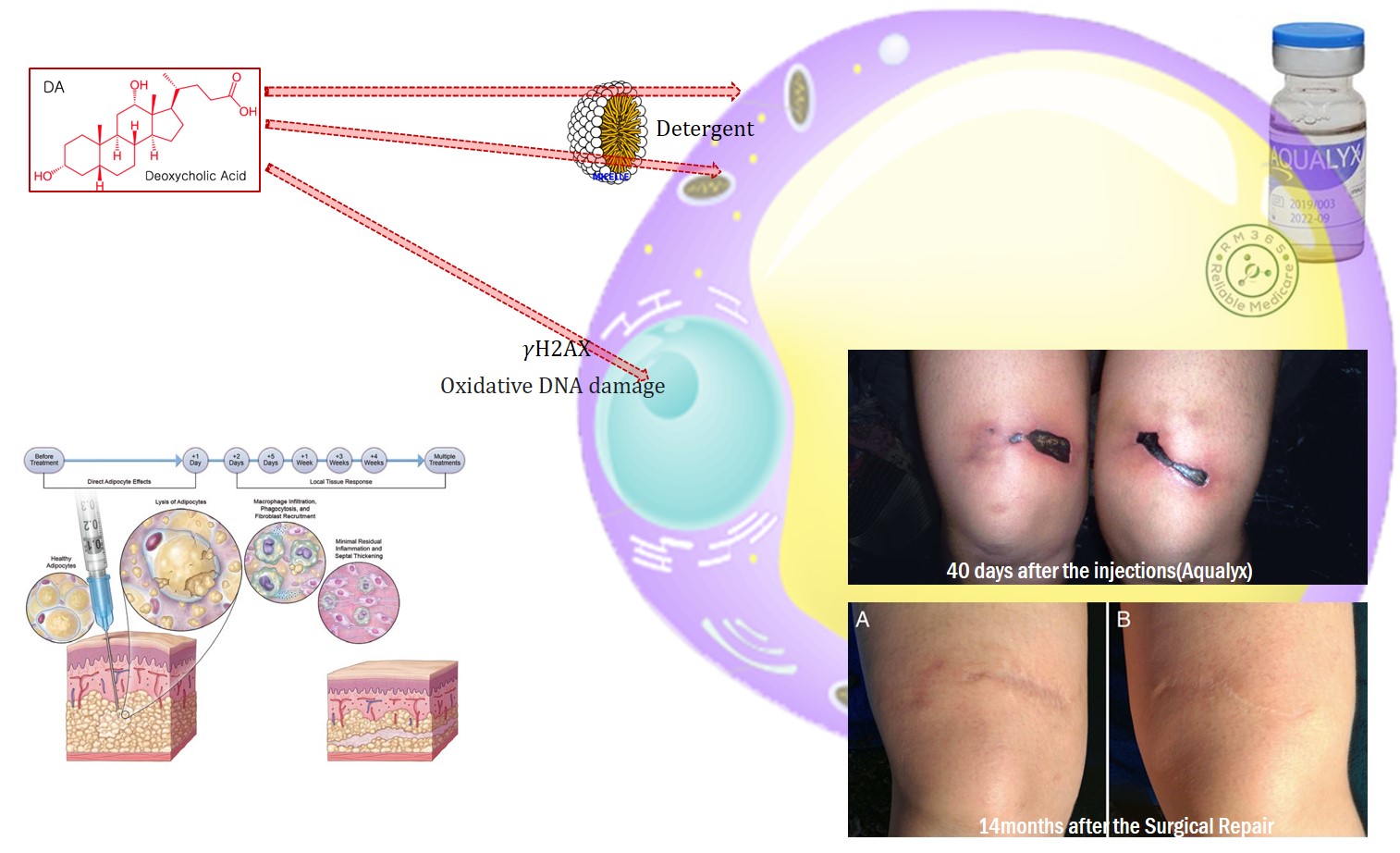 1.Lyse cells and solubilize cellular and membrane components by Micellization.
1.Lyse cells and solubilize cellular and membrane components by Micellization.
2.Lysis not only preadipocytes and adipocytes but also other kinds of tissue
3.Inflammatory Reaction by increasing macrophage markers, EMR1, NOS2, CD68, CD80, and IL1β
4.Product ROS/RNS( DNA Genotoxicity )
Methyl b-Cyclodextrin
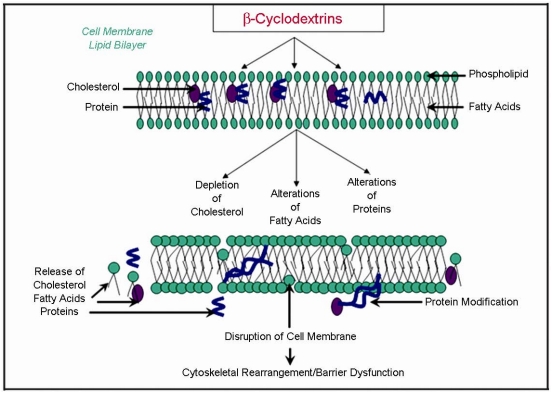
Osmotic Pressure
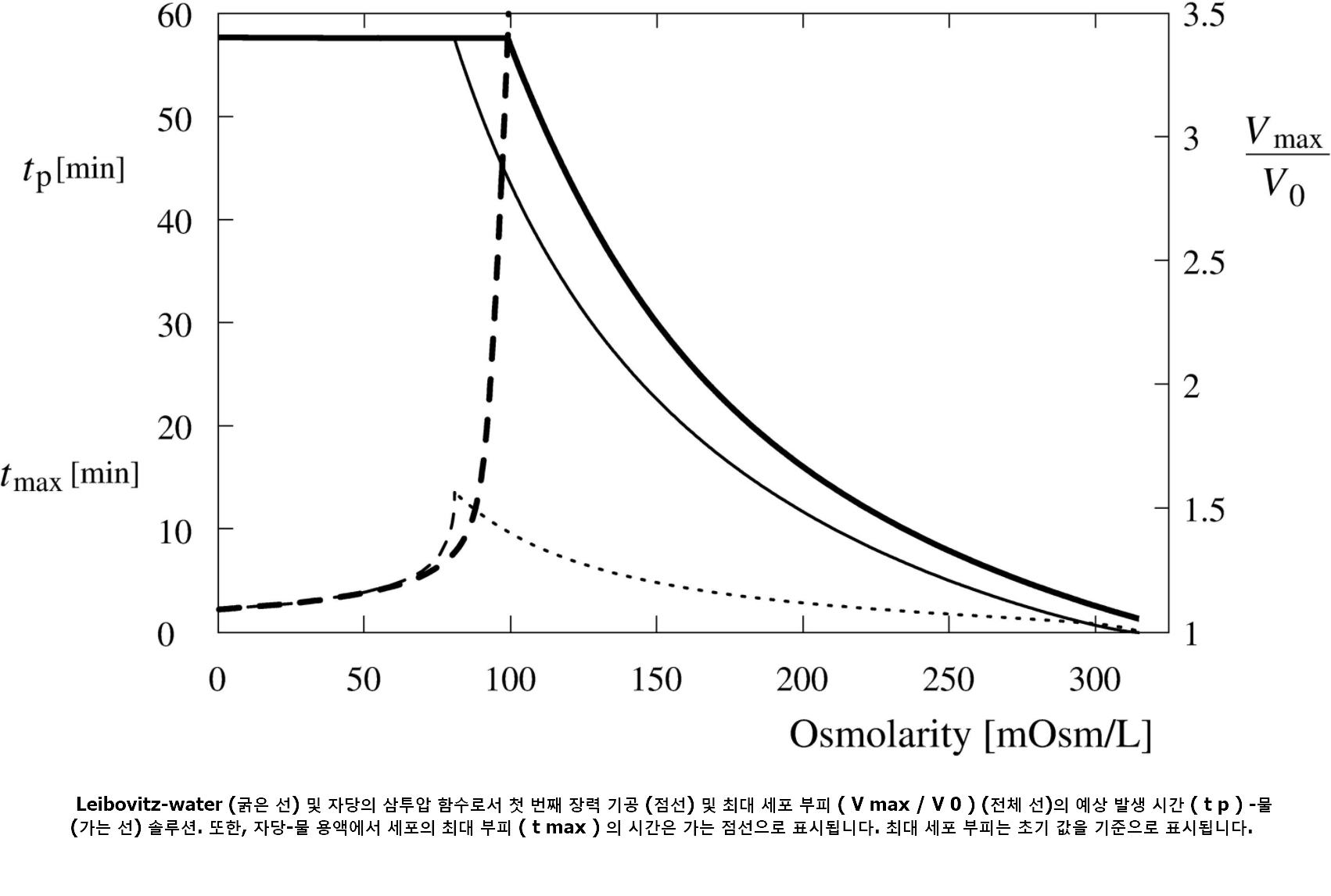
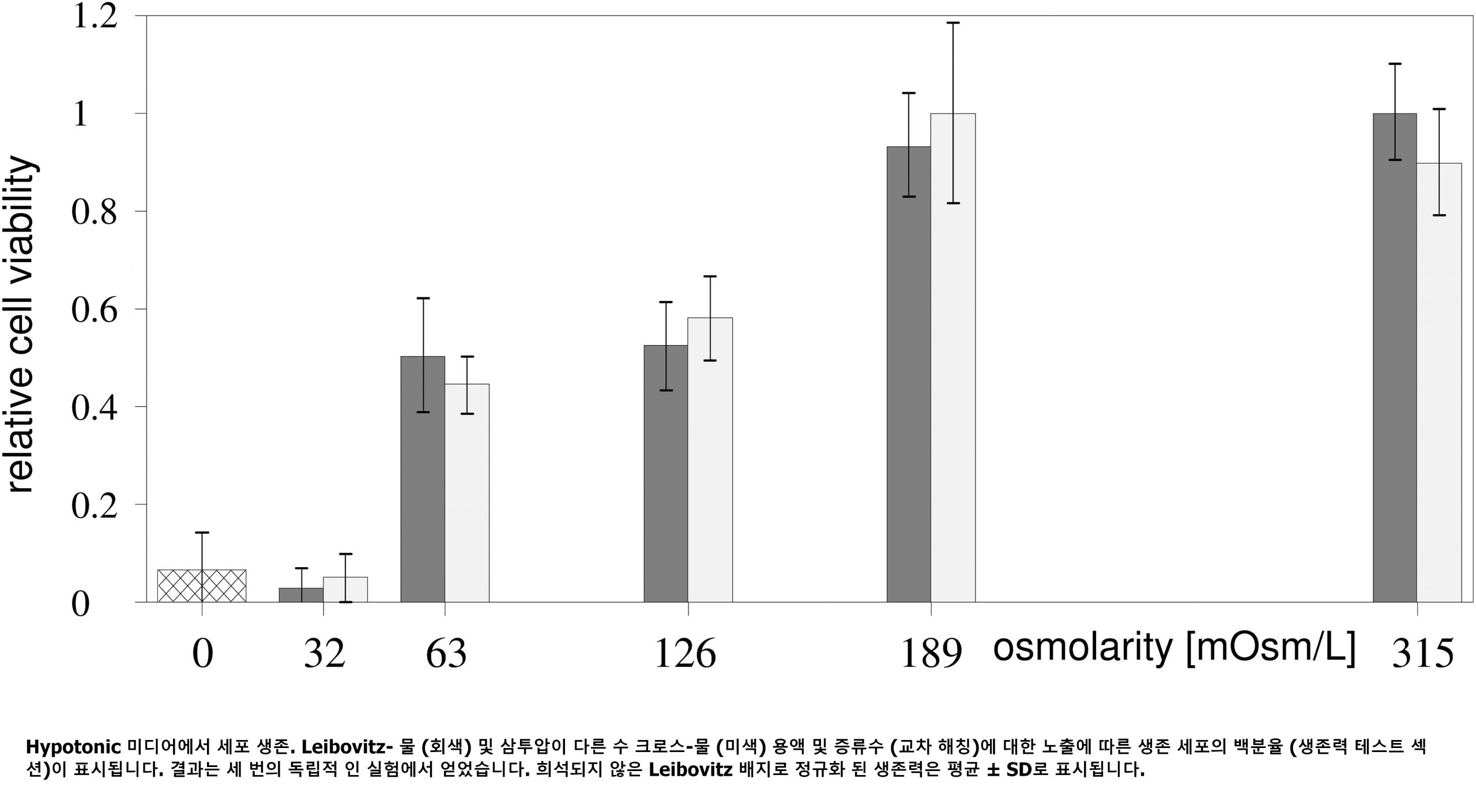

2. CHOLINE INDUCED LIPOLYSIS
Phosphatidylcholine
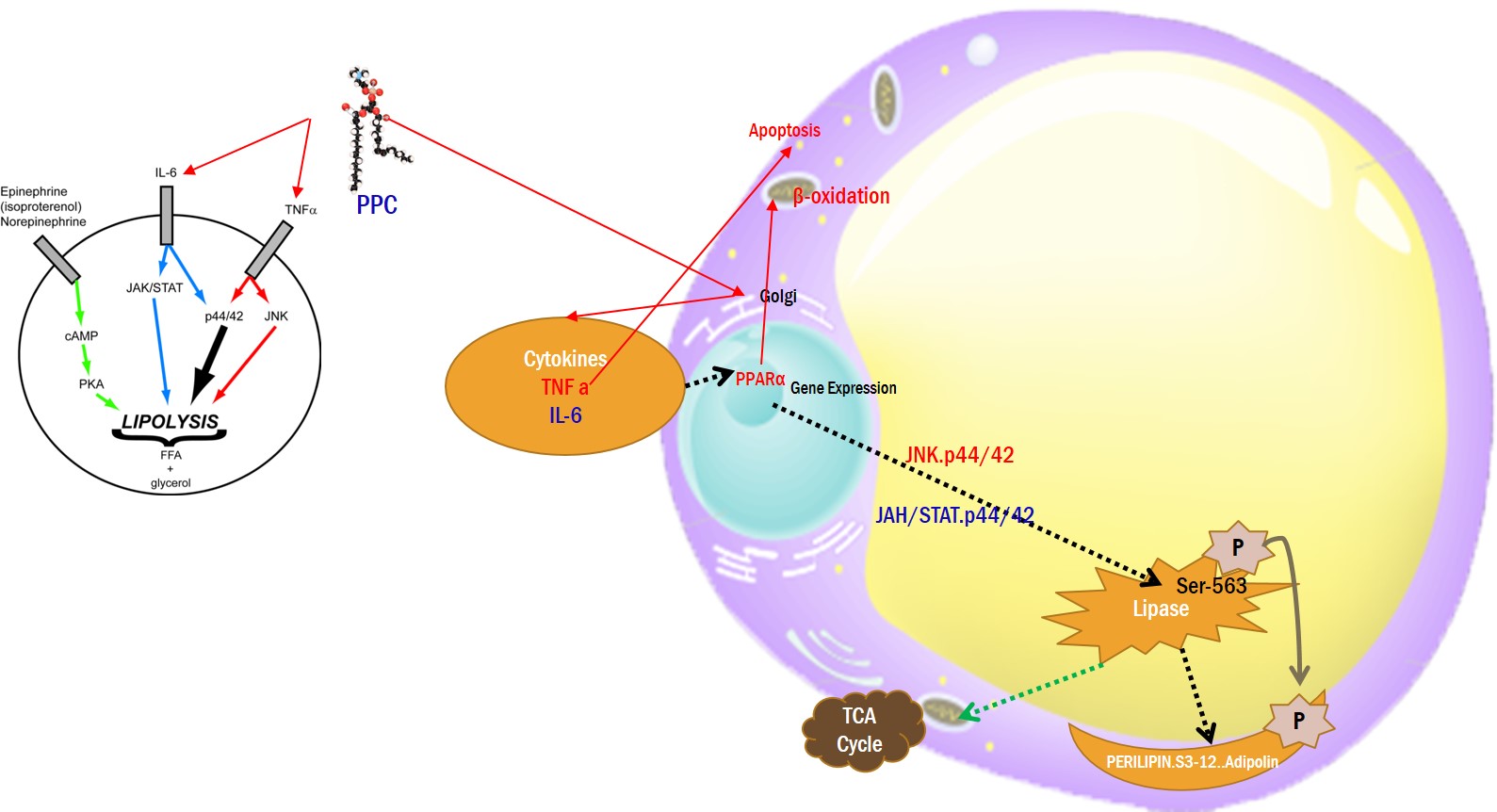 1)TNFα and IL-1β in PPC-mediated lipolysis and apoptosis in adipocytes, but not in non-adipocytes.
1)TNFα and IL-1β in PPC-mediated lipolysis and apoptosis in adipocytes, but not in non-adipocytes.
2) Suppressed the mRNA expression of adipokines (such as adiponectin and leptin)
3) Stimulate PPAR a Gene Expression
***10mg/ml 1%PPC Solution(50% Adipocyte cytolysis for 24hr. It can mix to maximum 6%),Phosphatidylcholine type S-PC-3 (soybean lecithin, hydrogenated, phosphatidylcholine content ≥98%) were provided by Lipoid GmbH, Ludwigshafen, Germany.
GPC (glycerophosphocholine )
1) Suppressed the mRNA expression ,suppresses 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation.
2) Stimulate PPAR a Gene Expression
3) From PPC by Diacylation
https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpcell.00305.2018
3. c-AMP, c-GMP INDUCED LIPOLYSIS
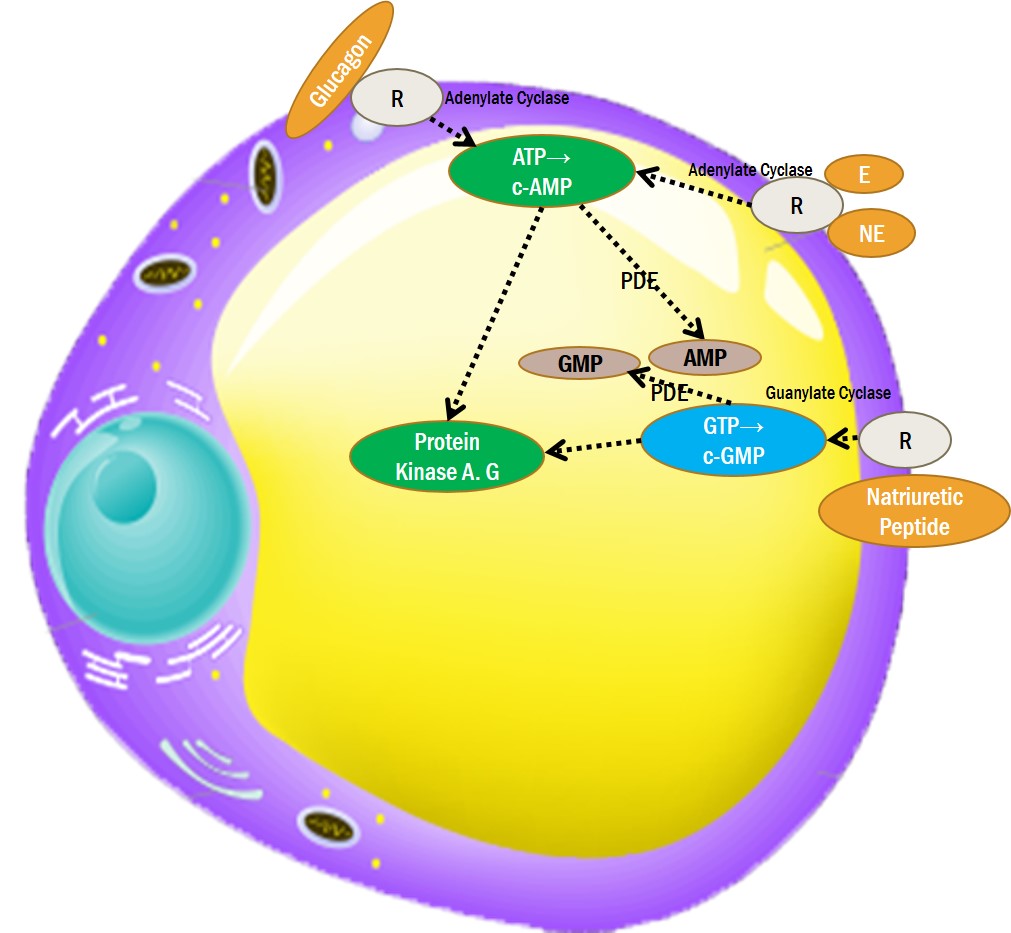
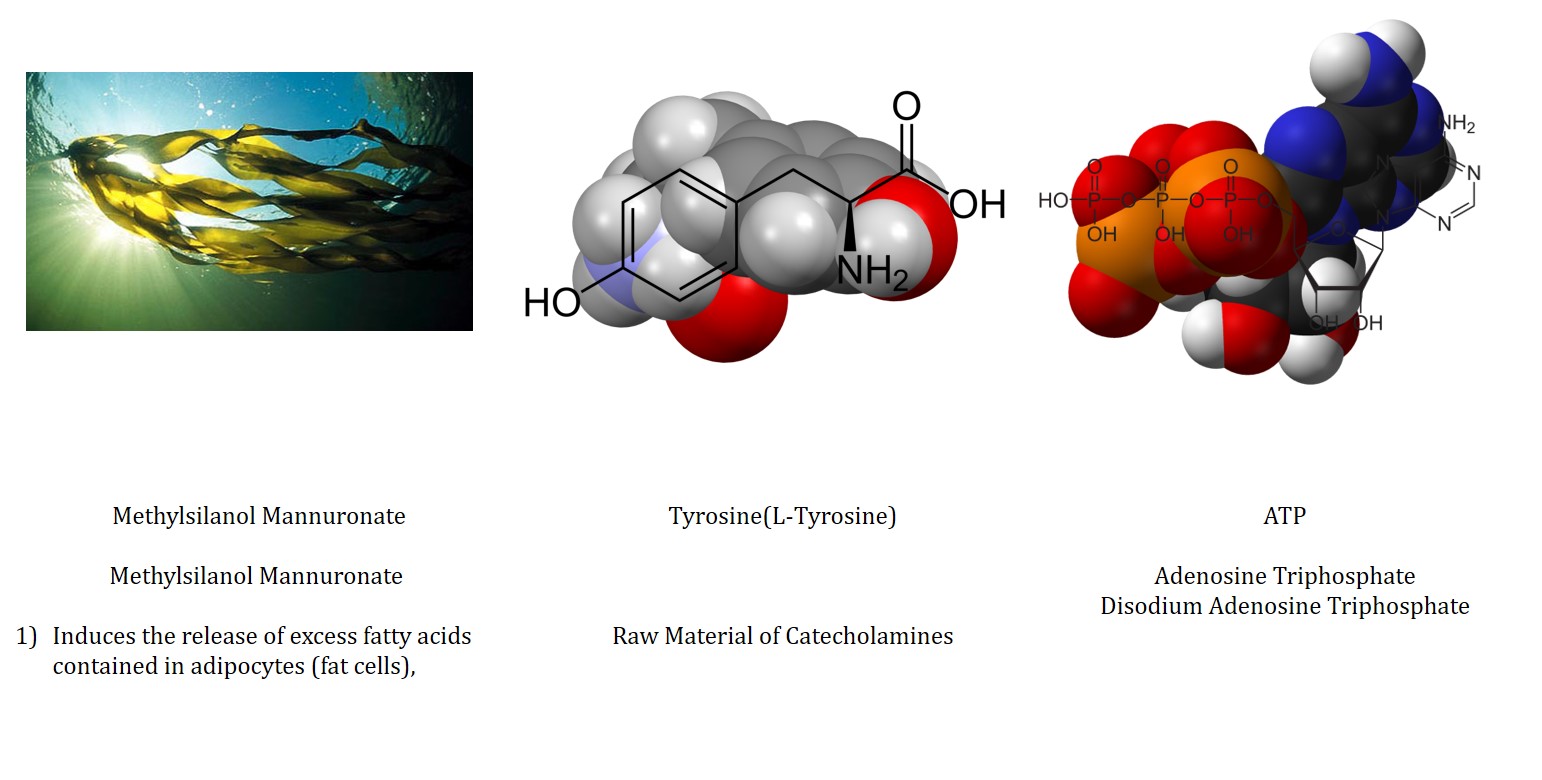
①β-ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST- Catecholamine, Tyrosine(L-Tyrosine), Phenylamine,Arginine ( increase GH-> β3-ADRENERGIC Receptor Agonist), Mirabegron
②GLUCAGON RECEPTOR AGONIST- Forskolin
Coleus Forskohlii Root Extract (포스콜리뿌리추출물)
③NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE RECEPTOR AGONIST- PNPs
Geranium Robertianum Extract (허브로버트추출물)
Nelumbo Nucifera Extract (연꽃추출물)
Arabidopsis Thaliana Extract(애기장대추출물)
④ADENYLATE & GUANYLATE CYCLATE ACTIVATOR- Forskolin
Coleus Forskohlii Root Extract(포스콜리뿌리추출물)
⑤PDH INHIBITOR LIPOLYSIS- Caffeine, Paraxanthine, Polyphenols, Caffeine Benzoate(카페인벤조에이트), Paraxanthine (파라잔틴)
*** Polyphenols(rutin, trans-ferulic acid, epigallaocatechin gallate , fumaric acid, chlorogenic acid , gallic acid , trans-resveratrol , propyl gallate , (+)-catechin, quercetin , kaempferol-3-O-β-D-galactoside)
Juglans Regia(Walnut) Seed Extract( 호두씨추출물)
Cynara Scolymus (Artichoke) Leaf Extract(아티초크 잎 추출물)
Camellia Sinensis Leaf Extract (녹차추출물)
Birch Leaf Extract (Betula Alba Leaf Extract) (만주자작나무잎추출물)
Acacia Catechu Catechins(카테츄카테킨)
3-1. β-ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST
Raw Material of Epi.NE : Tyrosine(L-Tyrosine), Phenylamine
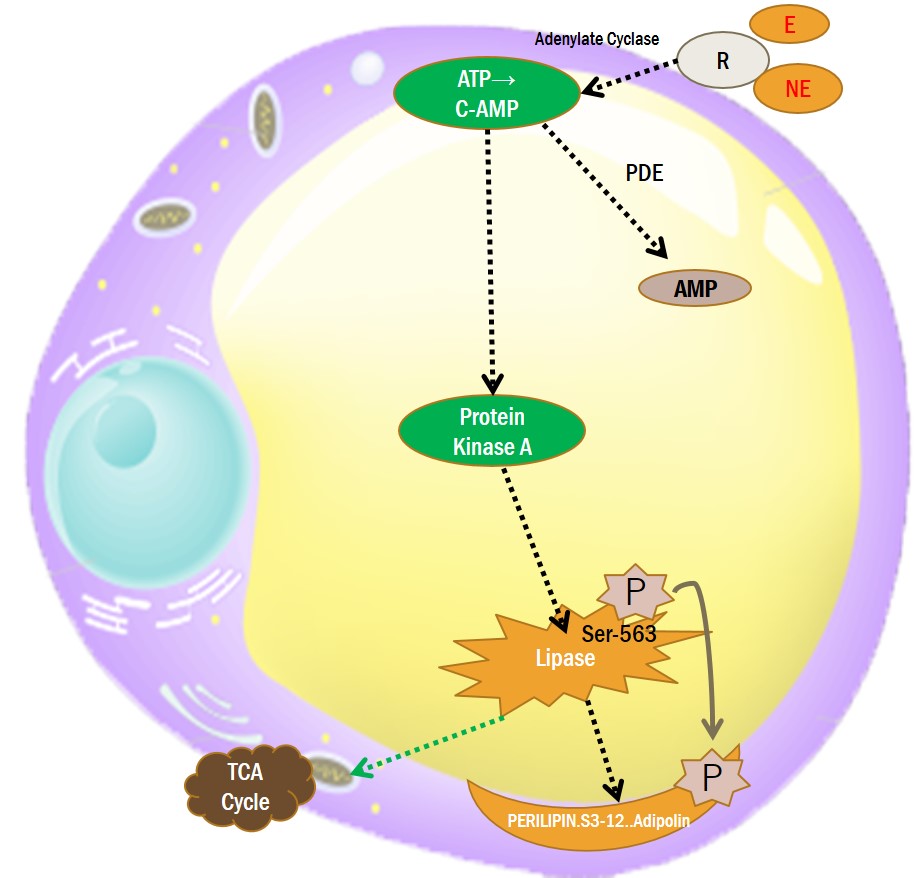 β1-adrenergic agonists
β1-adrenergic agonists
Denopamine, Isoproterenol
β2-adrenergic agonists
Salbutamol, Clenbuterol, Isoproterenol
β3-adrenergic agonists
Mirabegron
Solabegron
Amibegron
Growth Hormone
T3
Arginine ( increase GH-> β3-ADRENERGIC Receptor Agonist)
3-2. GLUCAGON RECEPTOR AGONIST
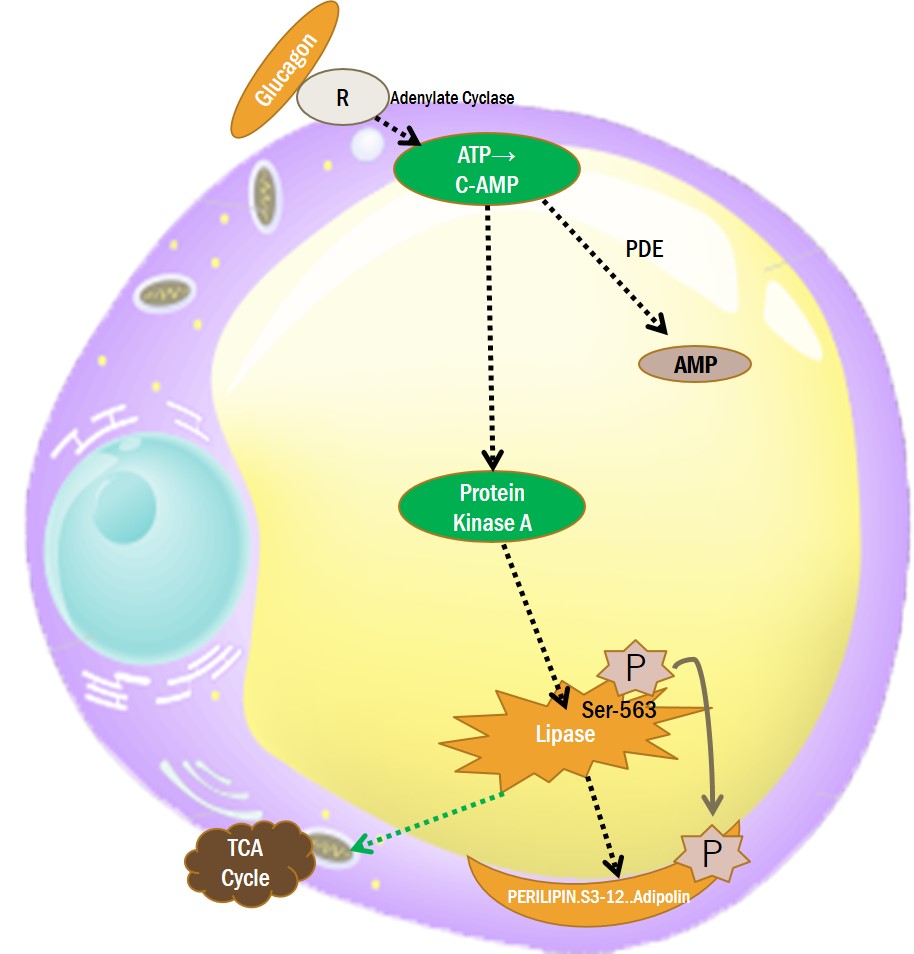 Glucagon
Glucagon
Glucagon-like peptide-1
Forskolin
3-3. NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE RECEPTOR AGONIST
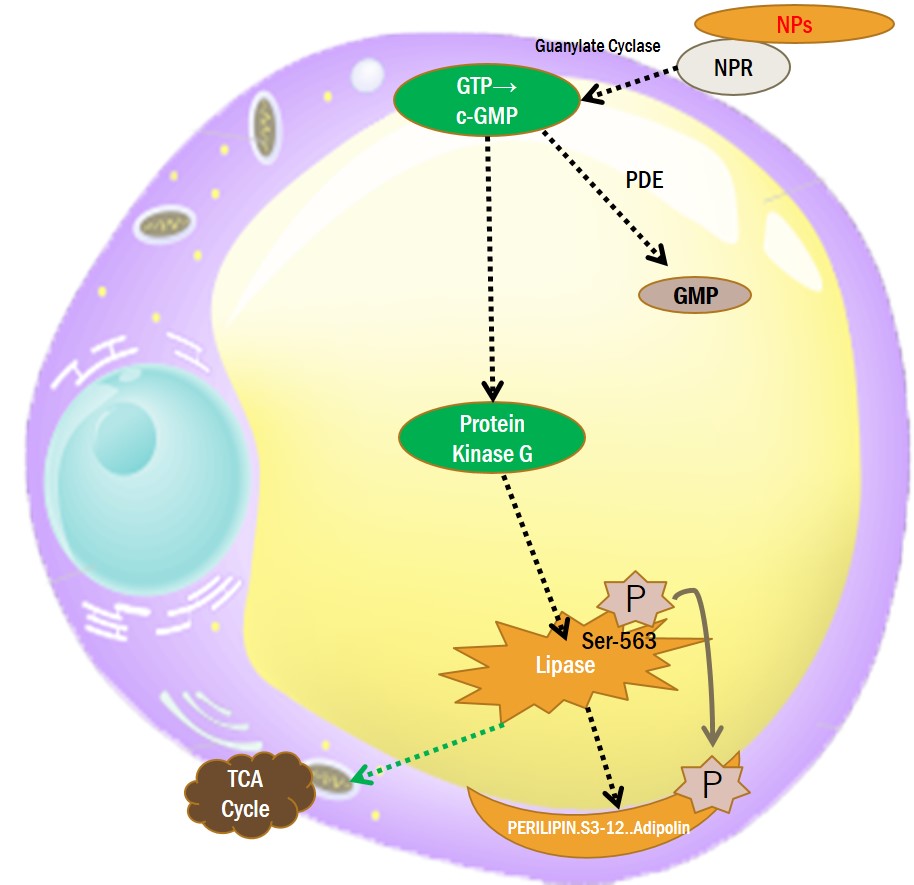 Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)
C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP)
D-type natriuretic peptide (DNP)
Urodilatin
Plant natriuretic peptides (PNPs) :
3-4. ADENYLATE & GUANYLATE CYCLASE ACTIVATOR
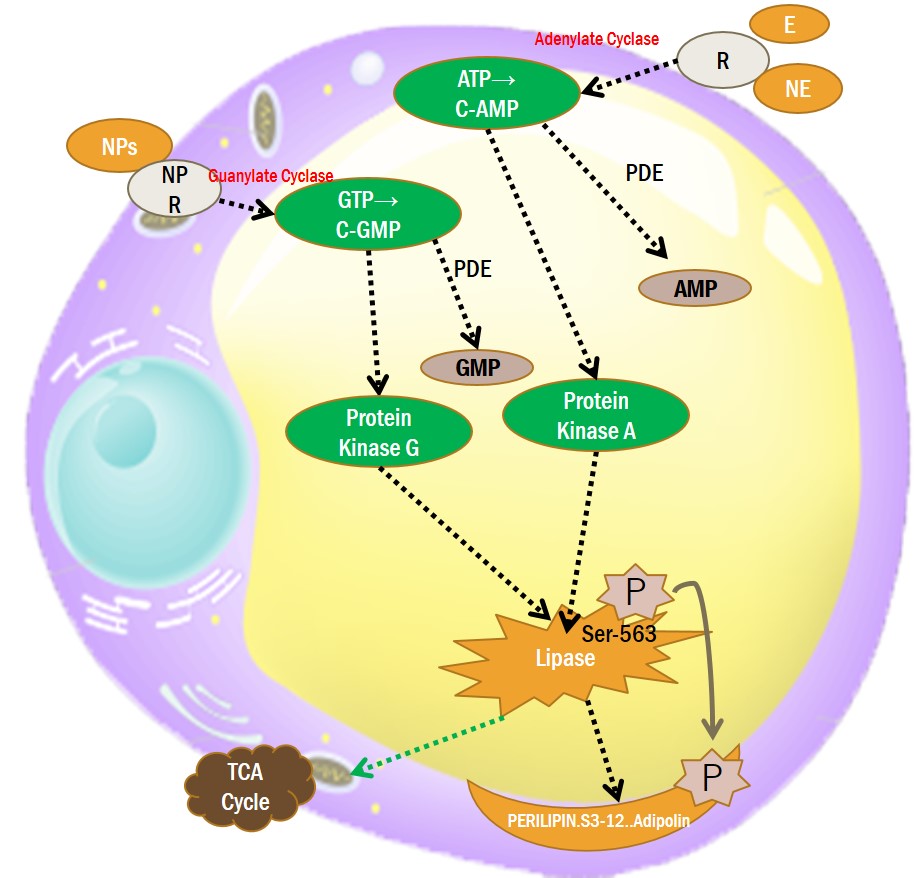
3-5. PDE (Phosphodiesterase) INHIBITOR
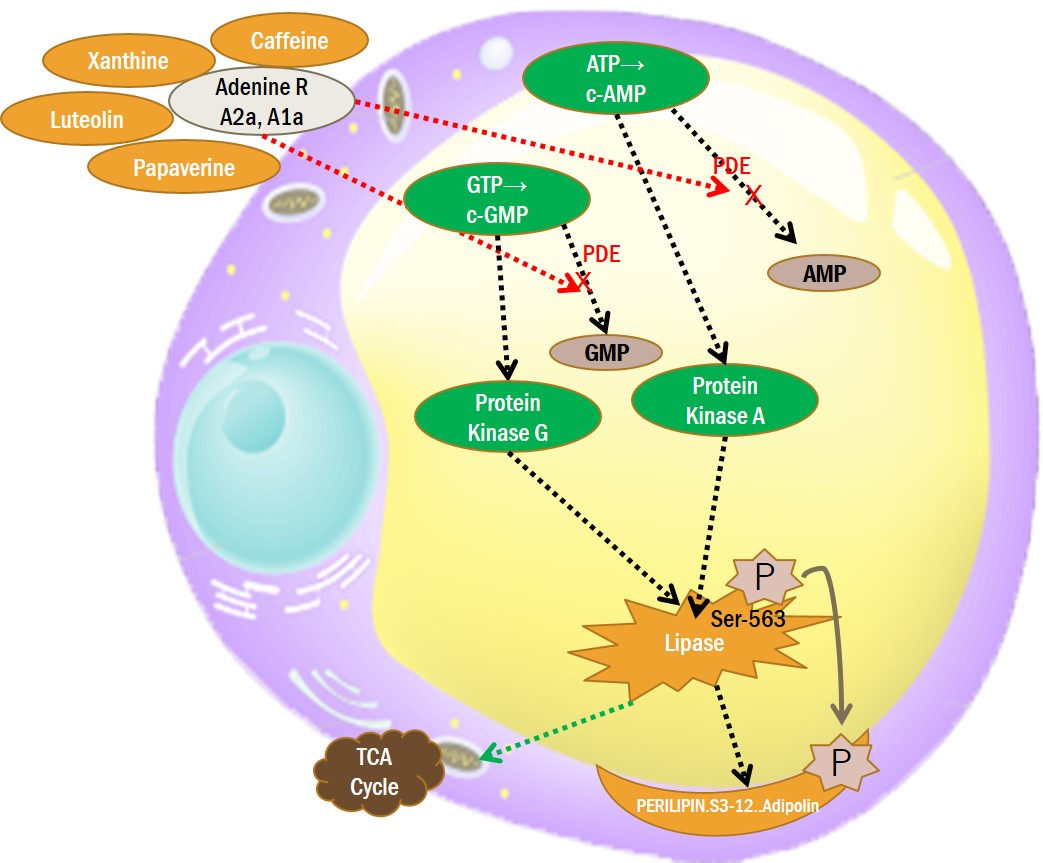
4. PKA(Protein Kinase A,D) ACTIVATING
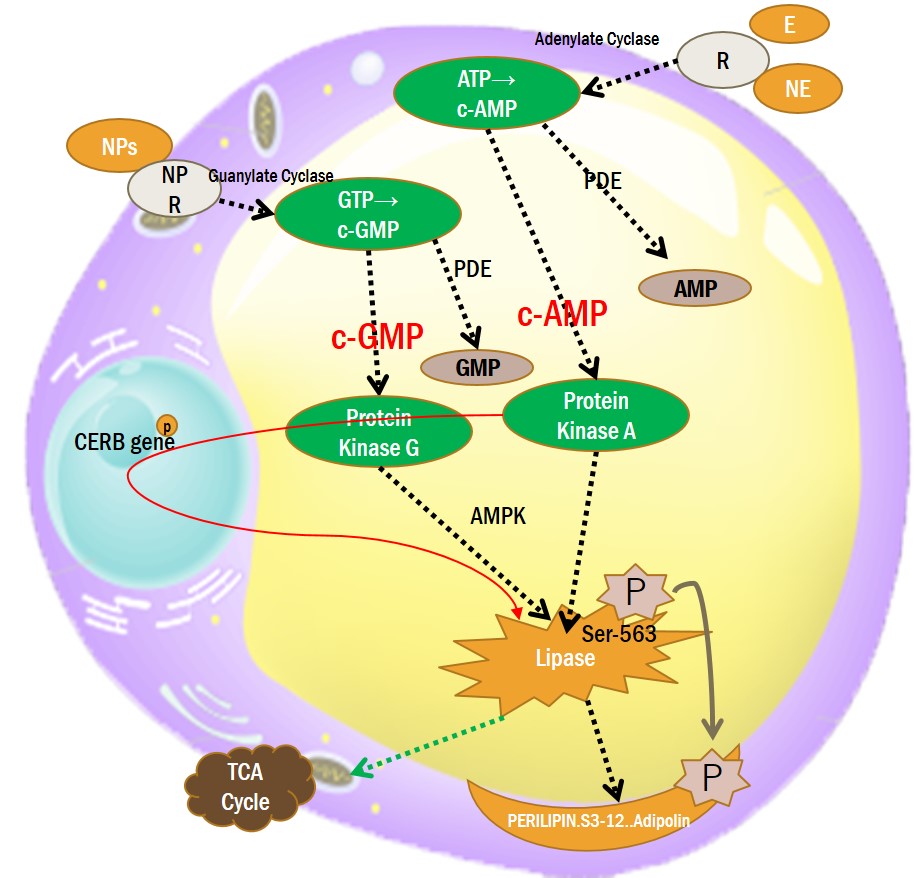
5. AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) ACTIVATING
5. PPARs (Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors) Regulation
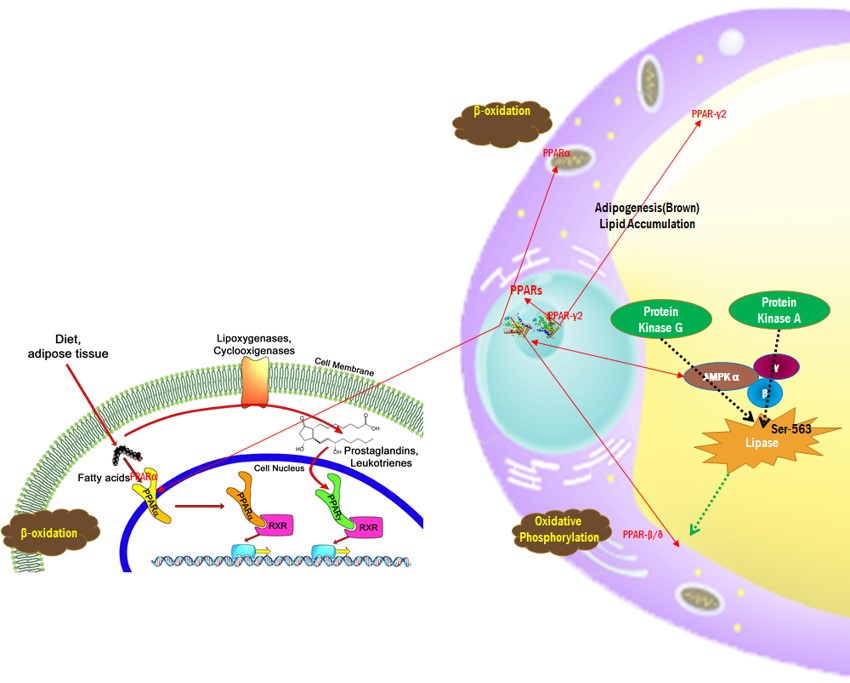 PPAR α : The PPAR-α agonist countered iBAT whitening by inducing the thermogenic pathway and reducing the lipid droplet size, in addition to enhanced VEGF-A expression, adrenergic stimulus, and lipolysis
PPAR α : The PPAR-α agonist countered iBAT whitening by inducing the thermogenic pathway and reducing the lipid droplet size, in addition to enhanced VEGF-A expression, adrenergic stimulus, and lipolysis
PPAR δ :Augmentation of β-oxidation in Mitochondria by UDP-1(uncoupling proteins-1) in Brown Adipocyte
PPAR γ : Differentiation and Maturation of preadipocyte to Matured Adipocyte with PPARγ and C/EBPα in white adipocyte.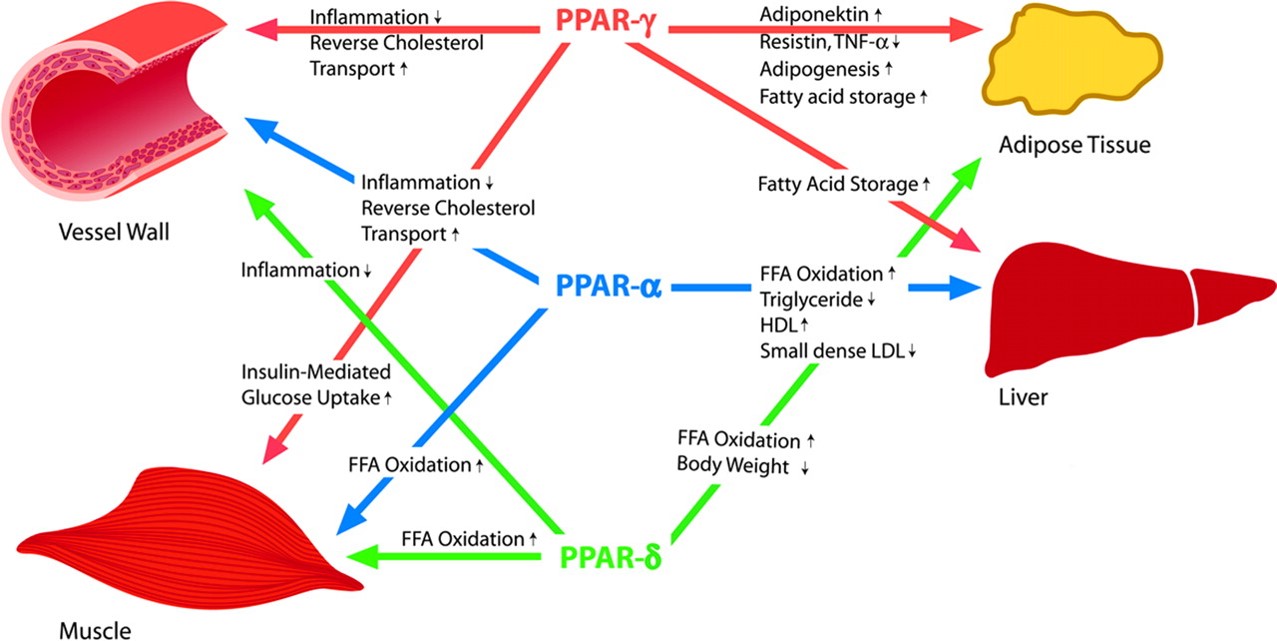
6. MITOCHONDRIA ENERGY PRODUCTION
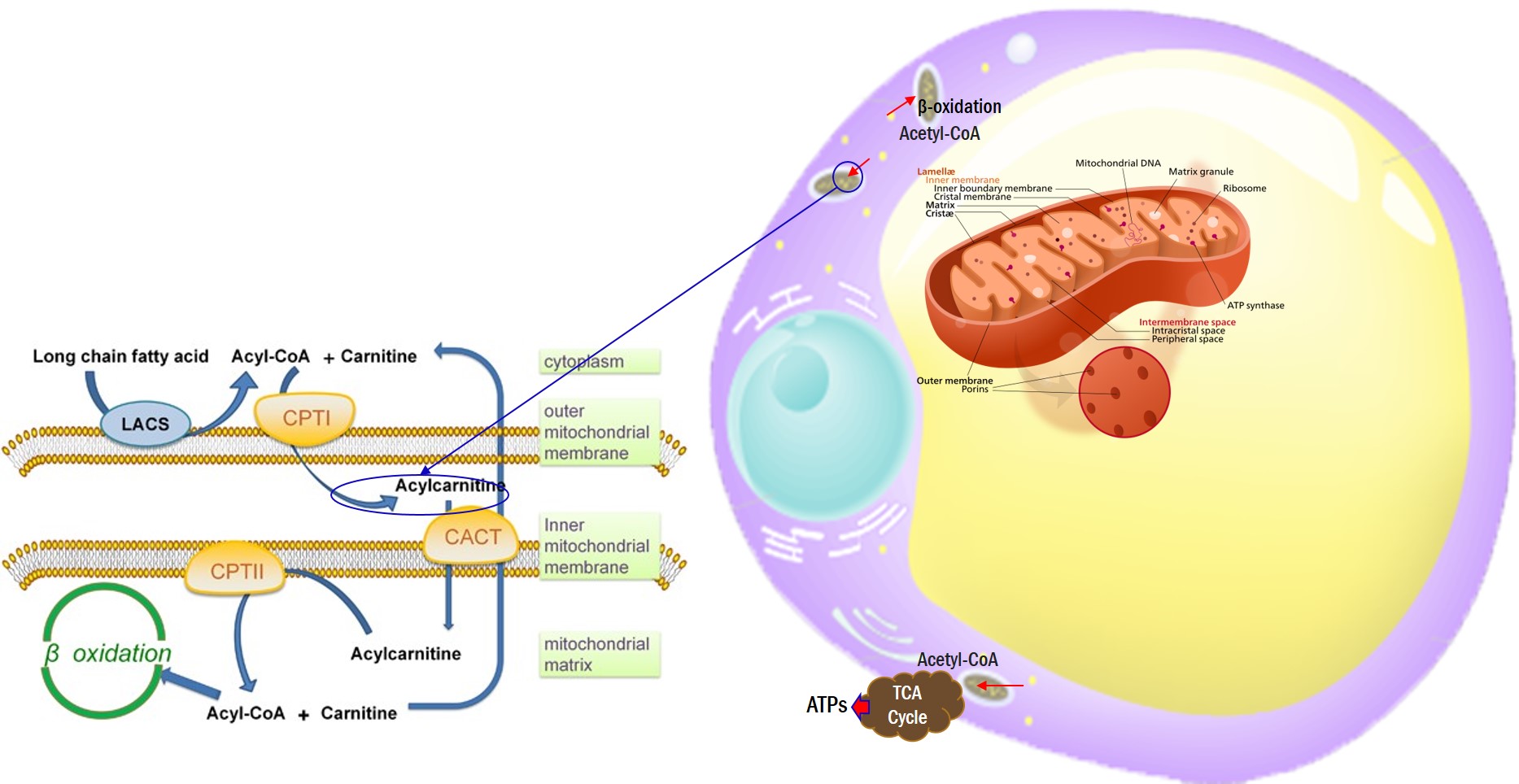
7. MISCELLANEOUS ORIGIN
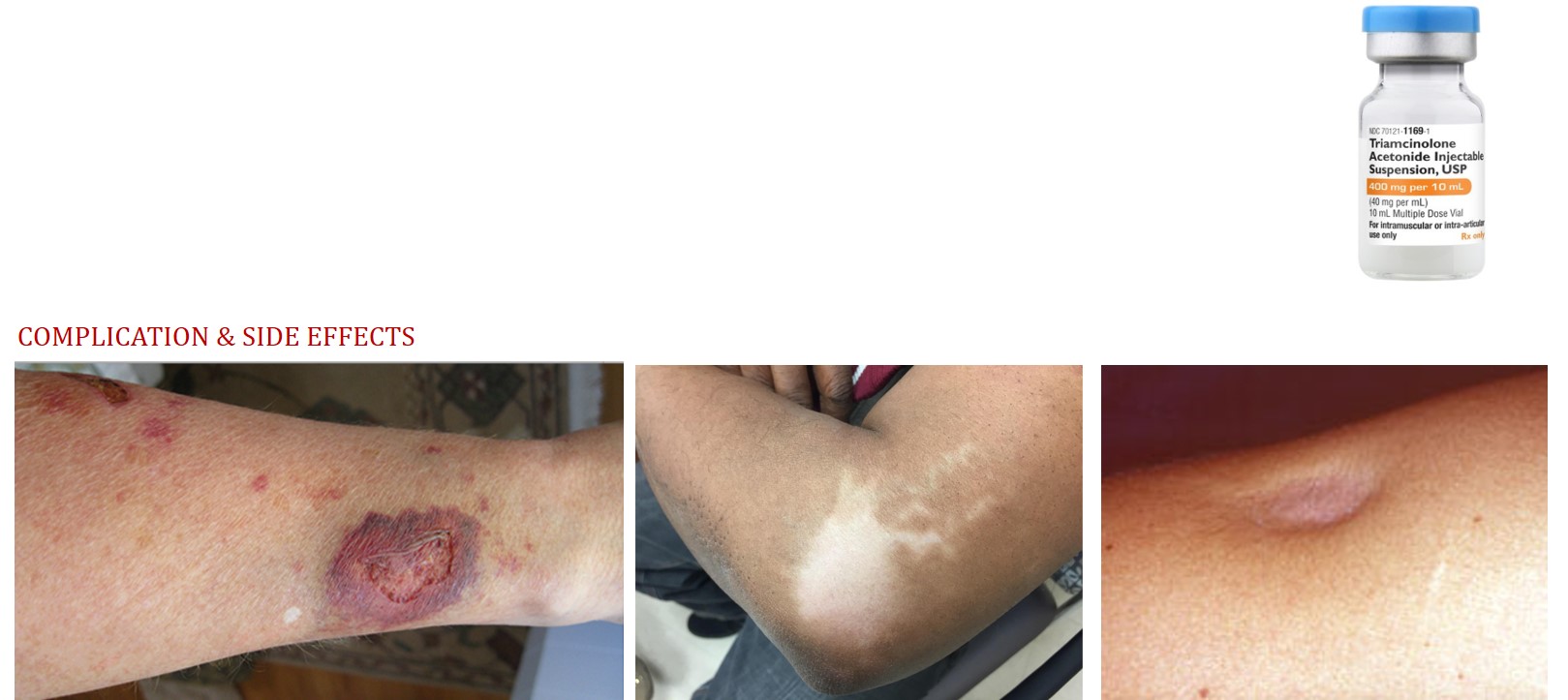
2.The corticosteroid-induced vasoconstriction, especially when administered locally in high concentrations. This enhanced vasoconstriction may facilitate local thrombosis or embolization and capillary closure with resultant local tissue hypoxia.
3.A glucocorticoid interferes with both the synthesis and degradation of type 1 collagen, and more drastically, type III collagen.
8. LIPOLYSIS TARGET POINTs
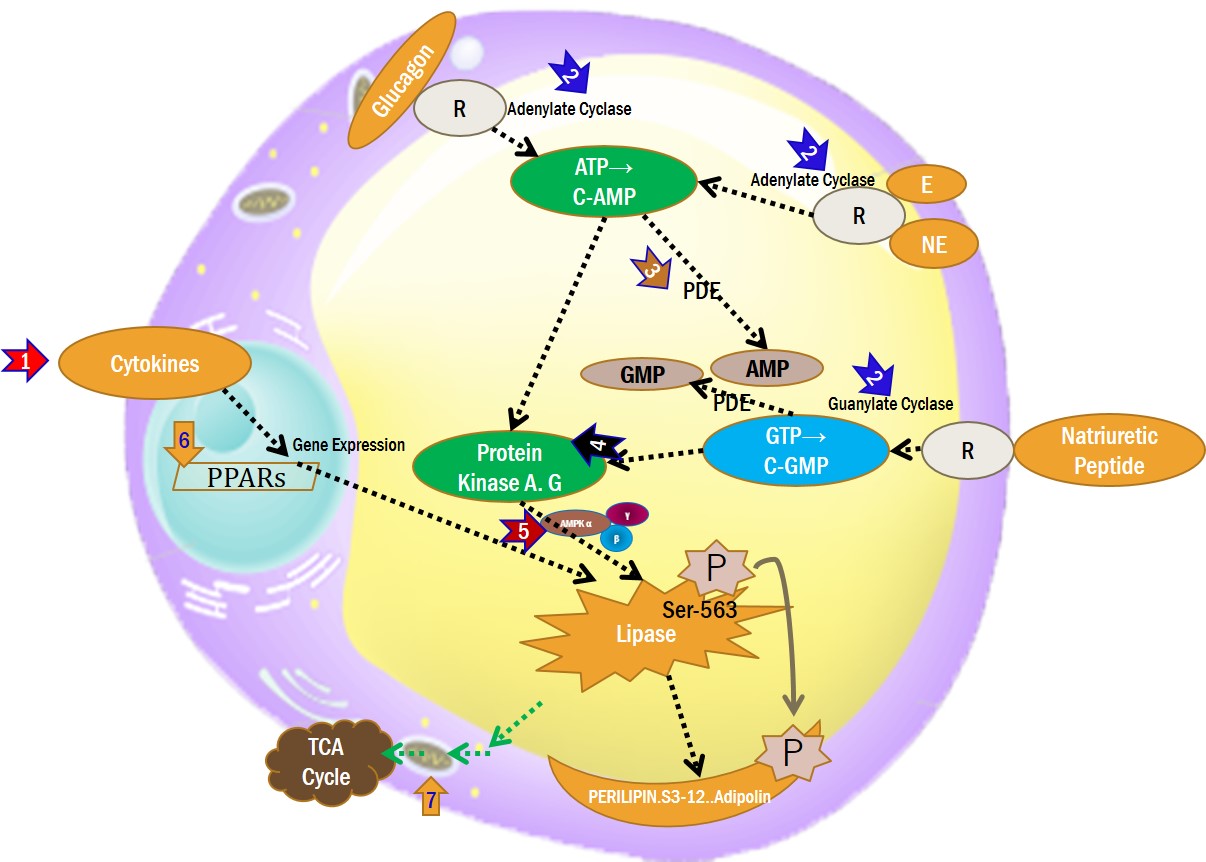 1.CYTOKINES INDUCED LIPOLYSIS, 2.c-AMP, c-GMP INDUCED LIPOLYSIS, ①β-ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST, ②GLUCAGON RECEPTOR AGONIST, ③NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE RECEPTOR AGONIST, ④ADENYLATE & GUANYLATE CYCLATE ACTIVATOR, 3.PDH INHIBITOR LIPOLYSIS, 4.Protein Kinases (PKA,PKG) Activating LIPOLYSIS, 5.AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) LIPOLYSIS, 6.PPARs INDUCED LIPOLYSIS, 7.MITOCHONDRIA ENERGY PRODUCTION LIPOLYSIS
1.CYTOKINES INDUCED LIPOLYSIS, 2.c-AMP, c-GMP INDUCED LIPOLYSIS, ①β-ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST, ②GLUCAGON RECEPTOR AGONIST, ③NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE RECEPTOR AGONIST, ④ADENYLATE & GUANYLATE CYCLATE ACTIVATOR, 3.PDH INHIBITOR LIPOLYSIS, 4.Protein Kinases (PKA,PKG) Activating LIPOLYSIS, 5.AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) LIPOLYSIS, 6.PPARs INDUCED LIPOLYSIS, 7.MITOCHONDRIA ENERGY PRODUCTION LIPOLYSIS DEOXYCHOLIC ACID
DEOXYCHOLIC ACID